26 Sep 2017
Zea mays - sweetcorn
It has been a good summer for growing sweetcorn. Many of us will be enjoying ample harvests from our gardens and allotments but sweetcorn is used for a lot more besides just eating!
When we take medications, in whatever form, how many of us realise that the active component is often only a small proportion of the formulation? The bulk of the medication (suppository, transdermal patch, solution, inhalation powder, tablet etc) that is not the active pharmaceutical ingredient has many different functions. Excipients facilitate the packaging of active ingredients. They can be used to enhance the absorption of the drug into the body, to alter the rate of absorption (i.e. to generate a slow release formulation) and to mask unpleasant tasting drugs.
Picture above: Sweetcorn growing in the SCIence Garden.
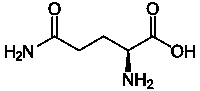
Glutamine
Prolamine proteins are a group of plant storage proteins that have a high proline and glutamine content.
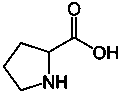
Maize is also an excellent source of starch - another commonly used excipient in tablets. Proline
Sweetcorn and long term science?
On a recent visit to the University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign, whilst walking through the campus, I spotted what looked like a field of sweetcorn growing in the middle of the campus. Now, I know in Illinois, fields of corn are everywhere but on a university campus?

Each sub-plot has been subjected to a different treatment - different levels of a range of nutrients, been part of a rotation system or not and above all everything is documented so the results can be further interpreted. Scientists have learnt that crop production does reduce the organic matter content of soils and lowers nutrient levels, requiring these to be added back in to the soil in order to maintain production levels.
Written by Alison Foster